I. Overview:
Most load types in power system belong to inductive load. In addition, power electronic devices are widely used in power enterprises, so the power factor of power grid is low. Lower power factor reduces equipment utilization ratio, increases power supply investment, damages voltage quality, reduces equipment service life, and greatly increases line loss. In order to improve the energy waste caused by the low power factor of power grid and these unfavorable factors of power supply production, it is necessary to effectively improve the power factor of power grid. Obviously, it is unreasonable and usually impossible for these reactive power to be supplied by generators and transmitted over long distances. Reasonable way is to generate reactive power where reactive power is needed, that is, to increase reactive power compensation equipment and devices.
II. Structure Composition
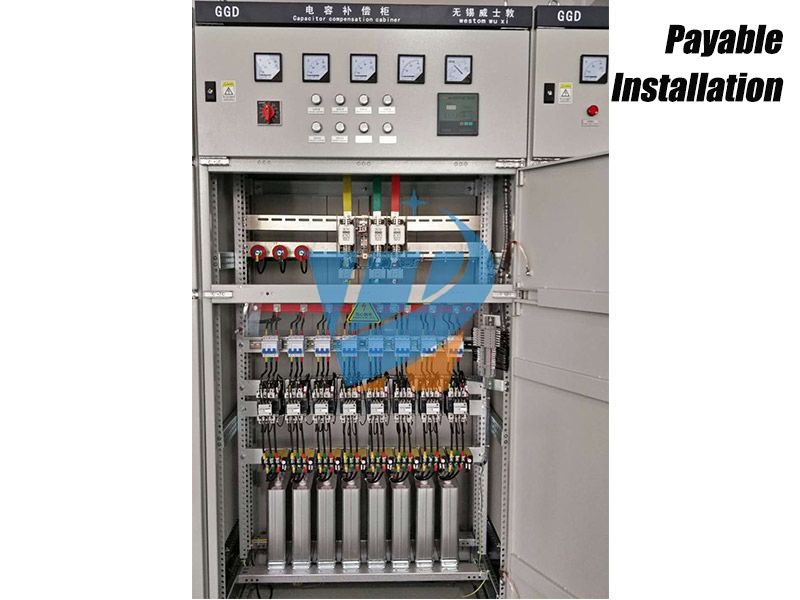
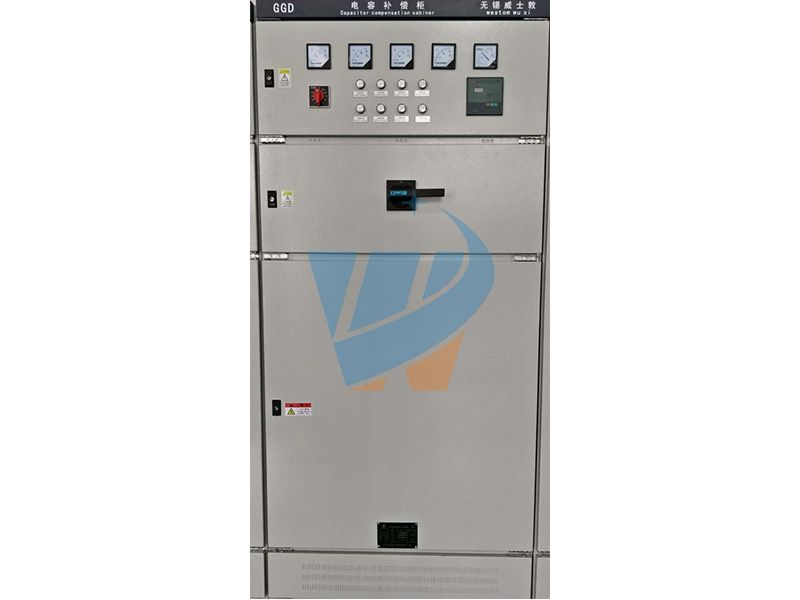
Generally speaking, low-voltage capacitance compensation cabinet is composed of cabinet shell, bus, circuit breaker, disconnector, thermal relay, contactor, lightning arrester, capacitor, reactor, primary and secondary conductor, terminal row, power factor automatic compensation control device, panel instrument, etc.
III. Basic Principles
In the actual power system, most of the loads are asynchronous motors. The equivalent circuit can be regarded as a series circuit of resistance and inductance. The phase difference between voltage and current is large and the power factor is low. After shunt capacitors are connected, the current of capacitors will offset part of the inductance current, so that the inductance current decreases, the total current decreases, the phase difference between voltage and current decreases, and the power factor increases.
A reactive power automatic controller is installed in the compensation cabinet, which automatically puts in or removes capacitors according to the load force rate. The main function of the controller is to make the load close to the required reactive current, thereby improving the power factor. For enterprises, the main reason is to avoid the penalty of power factor not up to the standard (0.9).
Ⅳ. Main Technical Indicators of Capacitance Compensation Cabinet
Rated operating voltage: AC380V + 15%
Rated operating frequency: 50Hz
Overload capacity: 120%, 1 minute
Switching frequency: 3.2 kHz (average)
Corresponding time: <10ms
Power loss of the device: When rated at full load, the loss does not exceed 2% of the compensation capacity.
Fifty harmonics and less can be filtered.
Manual and automatic tracking control
Noise: <60dB (1 meter away from device 1)
Protection Level: IP30
Structural Requirements: The cabinet body is installed on the ground with a length * width * height (mm) of 1000 * 1000 * 2260.
One-time Intake: Down Intake
Man-machine interface: Chinese display operation interface.
V. Product Completeness
The following documents and annexes shall be provided for supply:
1. Qualification Certificate
2. Packing list
3. Instructions for Use
4. Exit Inspection Report
5. Relevant electrical diagrams
6. Accessories for cabinet door keys and operating handles as stipulated in the contract
VI. Instructions for Order
1. Scheme diagram of main circuit system
2. Electrical schematic diagram of auxiliary circuit circuit
3. Plane layout of switchgear
4. Cabinet color (if not required, install provided by our company)
5. List of spare parts required
6. Other special requirements that do not meet the normal use of the product.
7. In the absence of master and auxiliary plans, the company may substitute for survey and design.